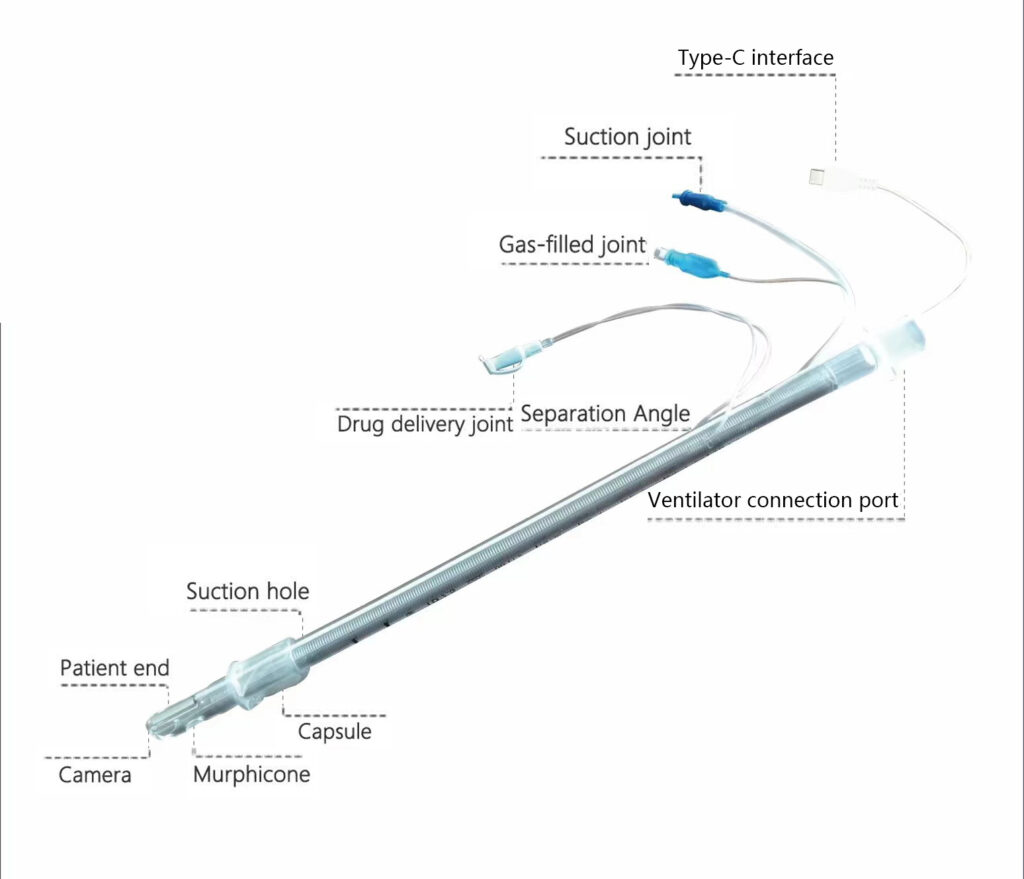
Video-assisted tracheal intubation has many advantages over traditional blind intubation techniques. These benefits include:
- Streamlining the airway management process: With video-assisted intubation, the assessment of the airway is simplified, and the process of intubation is made easier and more efficient.
- Safety for unexpected difficult airway patients: Video-assisted intubation is safe to use for patients with unexpected difficult airways, as it provides a clear visual of the airway.
- Accurate postoperative care for long-term intubated patients: Video-assisted intubation allows for accurate suctioning and medication administration to patients who require long-term intubation.
- Avoiding hypoxemia during airway tool exchanges: Video-assisted intubation eliminates the need for exchanging airway tools, which can cause hypoxemia.
- Shorter intubation time and higher success rate: With a reported 100% success rate in clinical studies, video-assisted intubation can shorten the intubation time and increase the success rate of intubation.
The Significance of Video-Assisted Tracheal Intubation
Video-assisted tracheal intubation is significant for several reasons:
- Confidence in product usage: The use of video-assisted intubation provides a clear visual of the airway, making the process of intubation less daunting.
- Evidence-based medicine: Full video recording of the intubation process can be used as evidence-based medicine.
- Avoidance of blind intubation complications: Video-assisted intubation can prevent complications such as hoarseness, laryngeal edema, and traumatic injury caused by blind intubation.
- Lowering the technical threshold: After simple training, all medical staff can perform video-assisted intubation, which can improve the emergency rescue capabilities of hospitals, especially in emergency departments, intensive care units, and respiratory departments.
- Lowering airway injury and care costs: Video-assisted intubation can reduce airway injury and care costs, lower the incidence of ventilator-associated pneumonia, and improve patient safety, ultimately shortening hospital stay and reducing costs.
- Preventing cross-infection: Video-assisted intubation eliminates the need to intubate while facing the patient, which can prevent cross-infection.
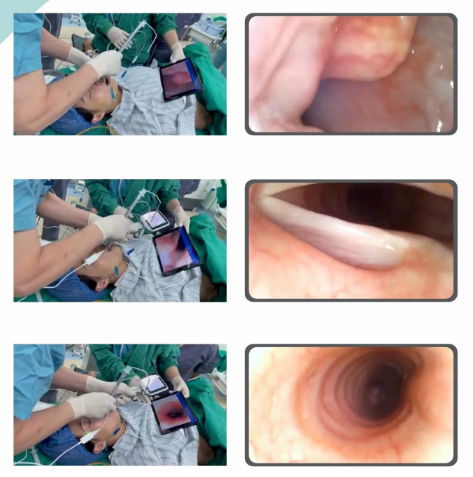

Common Complications of Blind Tracheal Intubation
Complications of blind tracheal intubation include:
- Accidental intubation of the esophagus: Although rare, accidental intubation of the esophagus can cause severe damage or death if not identified and corrected immediately.
- Hoarseness: Blind intubation can cause damage to the vocal cords and surrounding tissues, resulting in hoarseness.
- Unilateral bronchial intubation: Unilateral bronchial intubation can occur if the tube is inserted too deeply or not secured properly after removal.
- Local injury to the airway: Repeated intubation and improper fixation of the tube can cause local injury to the tracheal mucosa, leading to ulcers and granulomas.
- Subglottic stenosis: Subglottic stenosis occurs in long-term intubated patients, particularly children, due to damage to the subglottic tissue and weakened epithelium.
Additional Complications of Blind Tracheal Intubation
Other complications of blind tracheal intubation include:
- Trauma: Trauma to the teeth, oral cavity, nasal cavity, or pharynx can occur if the intubation process is too forceful.
- Adverse reactions to anesthesia: Intubation under light anesthesia can cause severe coughing or bronchospasm, leading to cardiac arrest or arrhythmia.
- Tube obstruction: The tube can become obstructed due to twisting or compression, leading to increased respiratory resistance and possible tube blockage.
- Laryngeal edema: If the tube is too large, it can cause laryngeal edema.
- Atelectasis: Unilateral bronchial intubation can cause atelectasis, leading to decreased ventilation in one lung.
